What is Stereo Chemistry ?
The branch of chemistry concerned with the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms and molecules and the effect of this on chemical reactions.What is Isomerism and its types?
The compounds having same molecular formula but different physical & chemical properties and also different structure called as isomers. This phenomenon is called as Isomerism.Chain isomerism
These isomers have same molecular formula but different carbon chain length. e.g, CH3-CH2-CH2-CH3 {n-Butane} & CH3-CH(CH3)-CH3 {iso-Butane}.Position isomerism
The compounds having same molecular formula, same carbon chain length but different position occupied by particular atom or group, this structures are called as position isomers. e.g, CH3-CH2-CH2-Br & CH3-CH(Br)-CH3, in this structures position occupied bt Br group is different at positionn1 and 2 respectively.Functional isomerism
The compounds having same molecular formula but different functional group attached are known as functional isomers. e.g, CH3-CH2-OH & CH3-O-CH3. Here, in first compound the functional group attached is Alcohol and in second compound it is Ether.Metamers
This type of isomerism is due to unequal distribution of Carbon atoms on either side of functional group. e.g, C2H5-O-C2H5 & CH3-O-CH2-C2H5. Here, in first compound there is same number of carbon atoms present on both sides of -O- atom but in second compound left side of ether group contain only one carbon atom and right side contain 3 carbon atoms.Geometrical isomers
Geometrical isomers are stereoisomers formed due to rotation of C-C bond. It is divided in 2 types:- Cis-isomers:
- Trans isomers:
When 2 similar groups present on same side of C-C bond.
It seen when same groups are present on opposite side of C-C bond.
Optical isomers
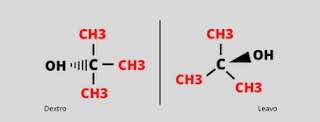
The property of substance to rotate Plane Polarized light is called as Optical activity. The compounds having same molecular formula but they rotates plane polarized light in opposite directions are called as Optical isomers. There are also two types of Optical isomers:- Dextrorotatory:
- Leavorotatory:
Substances which rotates plane polarized light towards right hand side are known as Dextrorotatory (d) substances.
Substances which rotates plane polarized light towards left hand side are known as Leavorotatoty (l) substances.
Enantiomers
Enantiomers are optical isomers and they are mirror images of each other. Properties :- They rotate plane polarized light in opposite direction.
- They have same melting point and solubility.
- Their reactivity is same.
- Their smell or odour is similar.
Diastereomers
Diastereomers are optical isomers having same molecular formula but they are not mirror images of each other. Properties :- They do not rotate plane polarized light in opposite direction.
- They have different melting point and solubility.
- Their reactivity is not same.
- Densities also varies.
Symmetries in molecules
A symmetry element is a line, a plane or a point in or through an object, about which a rotation or reflection leaves the object in an orientation indistinguishable from the original. There are main three types of symmetries as follow:- Plane of Symmetry:
- Centre of Symmetry:
- Axis of Symmetry:
The imaginary plane which divides molecule into two equal parts is known as plane of symmetry.
It is a point within molecule from which imaginary line drawn to opposite directions meet similar points at same distance and direction.
If a molecule is rotated about an axis through particular angle then new configuration is reflected in a plane perpendicular to axis then again initial configuration is obtained.